
Income Tax Allowances and Deductions Allowed to Salaried Individuals
Salaried employees are the backbone of the country’s taxpayer base, making significant contributions to tax revenue. Income tax deductions offer numerous opportunities for these individuals to save on taxes. By utilizing these deductions and exemptions, salaried individuals can substantially lower their tax liabilities.In this article, we outline the major deductions and allowances available to salaried individuals to help reduce their income tax burden.
Income Tax Allowances and Deductions
Allowances are amounts received by employees from their employers as part of their salary package, which may be exempt from tax under certain conditions.
Deductions are specific expenses or investments that can be subtracted from your gross total income, thereby reducing the taxable income.
Check out the Income Tax Allownaces and Deductions applied for Salaried Employees
1. House Rent Allowance (HRA)
House Rent Allowance (HRA) is a crucial benefit for salaried individuals who live in rented accommodation. The HRA received from the employer can be partially or fully exempt from taxes. The exemption is calculated as the minimum of the following:
- Actual HRA received.
- 50% of salary (for those living in metro cities) or 40% of salary (for non-metro cities).
- Rent paid minus 10% of salary.
Read more About HRA
2. Standard Deduction
The standard deduction is a straightforward deduction available to salaried employees. It was reintroduced in the 2018 budget and allows a flat deduction of Rs 50,000 from the gross salary, replacing earlier deductions for transport allowance and medical reimbursement.
3. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is an allowance provided by employers for travel within India. The LTA exemption can be claimed for travel expenses for the employee and their family during leave. The exemption is limited to actual travel costs and is available for two journeys in a block of four years.
Read More about LTA
4. Section 80C, 80CCC, and 80CCD(1): Investment-Based Deductions
Section 80C
Section 80C is the most extensively used option for saving income tax. Individuals can claim a deduction of up to Rs 1.5 lakh for investments and expenditures in specified avenues, such as:
- Life Insurance Premiums
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS)
- National Savings Certificates (NSC)
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- Tuition fees for children
- Principal repayment of home loans
- Tax-saving fixed deposits
Section 80CCC
This section allows deductions for contributions to pension funds, promoting savings for retirement.
Section 80CCD(1)
Section 80CCD(1) pertains to contributions to the National Pension System (NPS). It offers an additional deduction over the 80C limit, making it a valuable option for retirement planning.
5. Medical Insurance Premium (Section 80D)
Under Section 80D, individuals can claim deductions for medical insurance premiums paid for themselves, their family, and dependent parents. The deduction limits are:
- Up to Rs 25,000 for self, spouse, and children.
- Up to Rs 50,000 for senior citizen parents.
- An additional deduction of Rs 50,000 for individuals aged 60 and above.
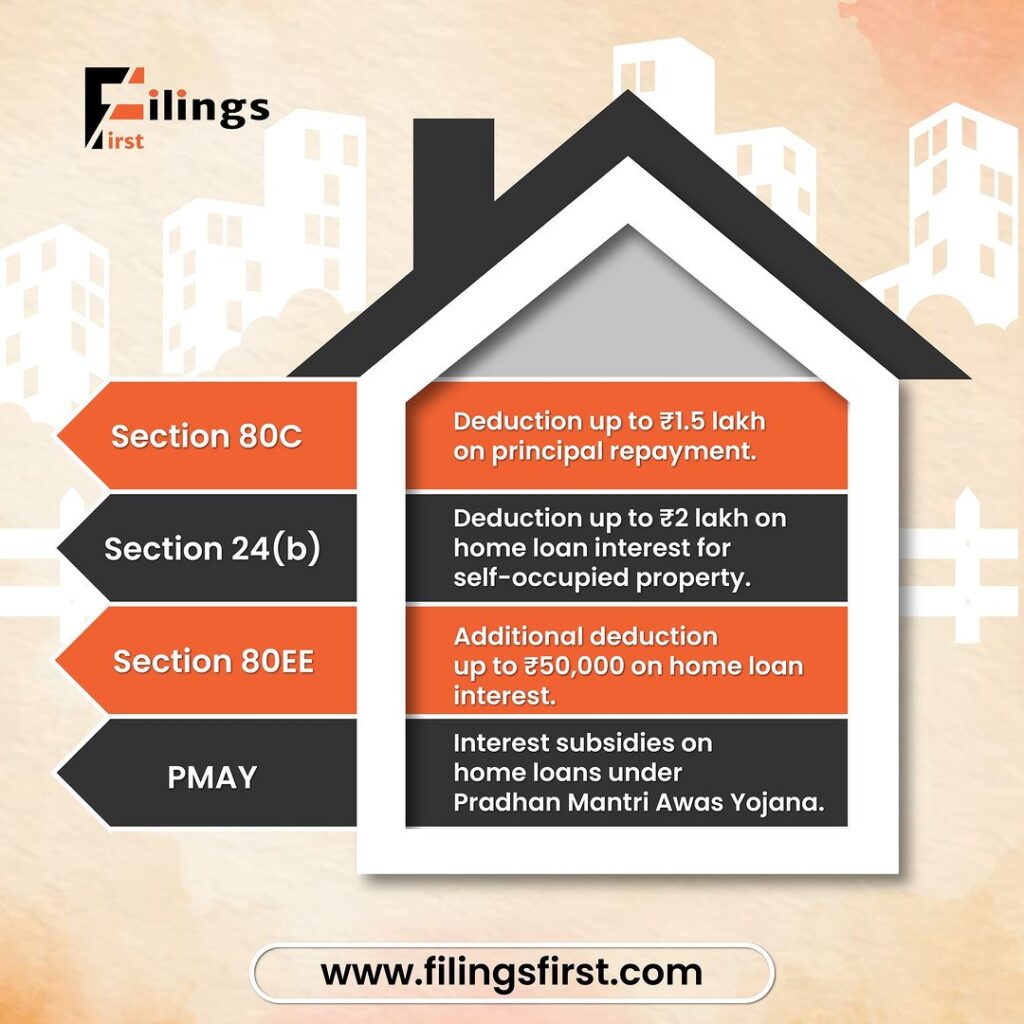
6. Interest on Home Loan (Section 24 and Section 80EE)
Section 24
Section 24 allows homeowners to claim a deduction of up to Rs 2 lakh on the interest paid on home loans for self-occupied properties.
Section 80EE
Section 80EE provides an additional deduction of Rs 50,000 on home loan interest for first-time homebuyers, subject to specific conditions such as:
- The loan amount should not exceed Rs 35 lakh.
- The property value should not exceed Rs 50 lakh.
- The individual should not own any other property at the time of loan sanction.
Read more about the IT Deduction List
7. Deduction for Education Loan Interest (Section 80E)
Section 80E offers deductions on the interest paid on education loans for higher studies. This deduction is available for up to 8 years or until the interest is fully repaid, whichever is earlier. It applies to loans taken for the individual, their spouse, children, or a legal ward.
8. Donations to Charitable Institutions (Section 80G)
Section 80G provides tax benefits for donations made to specified charitable institutions. The deduction can be either 50% or 100% of the donated amount, depending on the type of organization and subject to certain limits.
9. Savings Account Interest (Section 80TTA and 80TTB)
Section 80TTA
Section 80TTA allows a deduction of up to Rs 10,000 on interest earned from savings accounts for individuals and HUFs.
Section 80TTB
Section 80TTB provides a higher deduction limit of Rs 50,000 for senior citizens on interest earned from savings accounts, recurring deposits, and fixed deposits.
10. Professional Tax
Professional tax, deducted by the employer, is allowed as a deduction from gross salary under Section 16(iii).
Mobile Reimbursement
Employers often reimburse mobile phone expenses incurred for official purposes. This reimbursement is tax-exempt if supported by actual bills and is within reasonable limits.
Benefits:
- Reduces taxable income
- Requires accurate record-keeping and bill submission
Books and Periodicals
Expenses on books, newspapers, journals, and periodicals used for work-related purposes can be reimbursed by the employer. This reimbursement is tax-exempt when supported by receipts.
Benefits:
- Supports professional development
- Reduces taxable income
Food Coupons
Food coupons or meal vouchers provided by the employer are tax-exempt up to Rs 50 per meal. These coupons can be used at various restaurants and food outlets.
Table: Tax-Exempt Meal Voucher Limit
Meal Type | Exemption Limit |
Per Meal | Rs 50 |
Benefits:
- Reduces taxable income
- Enhances employee satisfaction
Relocation Allowance
When an employee relocates due to a job transfer, the employer may provide a relocation allowance to cover moving expenses. This allowance can be tax-exempt if it covers actual expenses such as transportation of goods, travel, and temporary accommodation.
Benefits:
- Reduces taxable income
- Covers significant relocation costs
Children's Education Allowance
Salaried individuals can claim an exemption for the Children’s Education Allowance provided by the employer.
Table: Children’s Education Allowance
Allowance Type | Exemption Limit |
Children’s Education | Rs 100/month/child (max 2 children) |
Children’s Hostel Accommodation | Rs 300/month/child (max 2 children) |
Benefits:
- Helps manage education costs
- Reduces taxable income
Gratuity
Gratuity received by an employee on retirement or termination is tax-exempt up to a certain limit under the Payment of Gratuity Act.
Table: Gratuity Exemption Limits
Coverage | Exemption Limit |
Employees covered under Act | Rs 20 lakh |
Employees not covered | Rs 10 lakh |
Benefits:
- Recognizes long-term service
- Provides a tax-free lump sum payment
Tax Treatment on Notice Pay and Joining Bonus
Notice Pay
If an employee leaves a company before the notice period ends, the notice pay recovered by the employer is not taxable as salary income. If the new employer reimburses the notice pay, it becomes taxable.
Joining Bonus
A joining bonus received from the employer is taxable as salary income. If the employee repays the joining bonus due to non-fulfillment of service conditions, the repaid amount cannot be claimed as a deduction.
Exemptions on Perquisites
Employers often provide various perks to employees, some of which are exempt from tax.
Table: Common Perquisites and Exemptions
Perquisite | Exemption Criteria |
Cab Facility | Provided for commuting to and from the workplace |
Health Club Facility | Provided uniformly to all employees |
Gifts or Vouchers | Up to Rs 5,000 per year |
Medical Expenditure Abroad | Subject to conditions, for employee or family |
Training and Development | Expenses borne by the employer |
Perquisites Outside India | Allowed by the government to Indian citizens abroad |
Refreshments | Provided during working hours on office premises |
Benefits:
- Reduces taxable income
- Enhances employee benefits and satisfaction
Understanding and utilizing the various tax allowances and deductions available can significantly reduce your taxable income and increase your savings. It’s essential to keep abreast of the latest tax laws and consult with a tax professional if needed to make the most of these benefits. By effectively planning your taxes, you can ensure that you retain more of your hard-earned money.
FAQs
1: What is the significance of income tax deductions for salaried individuals?
Income tax deductions provide salaried individuals with opportunities to reduce their taxable income, thereby lowering their overall tax liability and increasing their take-home pay.
2: Can mobile reimbursement be claimed as a tax exemption?
Yes, mobile reimbursement provided by the employer for official purposes is tax-exempt, provided it is supported by actual bills and within reasonable limits.
3: Are expenses on books and periodicals tax-deductible?
Yes, expenses on books, newspapers, journals, and periodicals used for work-related purposes can be reimbursed by the employer and are tax-exempt when supported by receipts.
4: What is the tax-exemption limit for food coupons?
Food coupons or meal vouchers provided by the employer are tax-exempt up to Rs 50 per meal.
5: How does the relocation allowance work for tax purposes?
Relocation allowance provided by the employer to cover moving expenses due to job transfer can be tax-exempt if it covers actual expenses such as transportation, travel, and temporary accommodation, supported by receipts.
6: What are the exemptions for children’s education and hostel allowances?
The Children’s Education Allowance is tax-exempt up to Rs 100 per month per child for a maximum of two children. The Children’s Hostel Allowance is tax-exempt up to Rs 300 per month per child for a maximum of two children.
7: Is gratuity received on retirement taxable?
Gratuity received on retirement or termination is tax-exempt up to Rs 20 lakh for employees covered under the Payment of Gratuity Act and up to Rs 10 lakh for those not covered.
8: How is notice pay treated for tax purposes?
Notice pay recovered by the employer if an employee leaves before the notice period ends is not taxable as salary income. However, if reimbursed by the new employer, it becomes taxable.
9: What are the tax implications of a joining bonus?
A joining bonus received from the employer is taxable as salary income. If repaid due to non-fulfillment of service conditions, the repaid amount cannot be claimed as a deduction.
10: What perquisites are exempt from tax?
Common tax-exempt perquisites include cab facilities for commuting, health club facilities provided uniformly to all employees, gifts or vouchers up to Rs 5,000 per year, medical expenditure abroad under certain conditions, training and development expenses, and refreshments provided during working hours.
11: How can I maximize my tax savings as a salaried individual?
To maximize tax savings, take full advantage of available deductions and exemptions, maintain accurate records, submit necessary documentation, and stay updated with the latest tax laws. Consulting a tax professional can also help in effectively planning your taxes.


